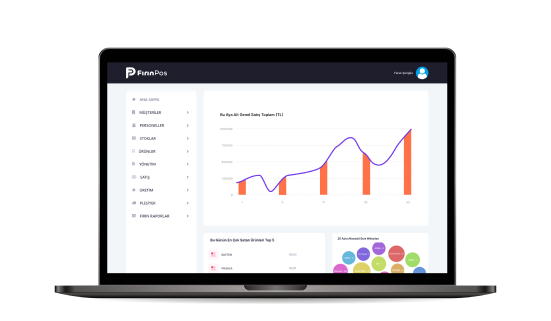
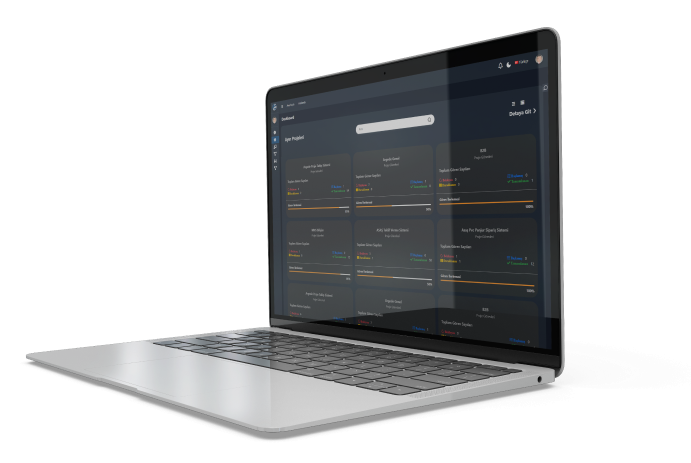
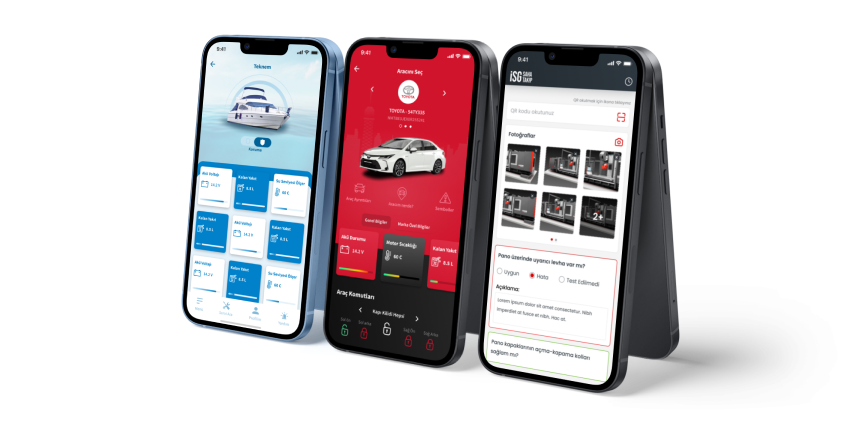
User Experience (UX) and Interface (UI) Design
The accessibility and prevalence of personal and office computers meant that interfaces had to be designed with users in mind. If users can't interact with their computers, they won't sell. As a result, the UI designer was born. As with all emerging technologies, the UI designer's role has evolved as systems, preferences, expectations and accessibility demand more and more of devices.
UI designers now work not only on computer interfaces, but also on "invisible" or screenless interfaces (also called zero UI) such as mobile phones, augmented and virtual reality, and even sound, motion, and light. Today's UI designer has nearly unlimited opportunities to work on websites, mobile apps, wearable technology and smart home devices. As long as computers continue to be a part of daily life, there will be a need to make interfaces that users of all ages, all types and technical backgrounds can use effectively.
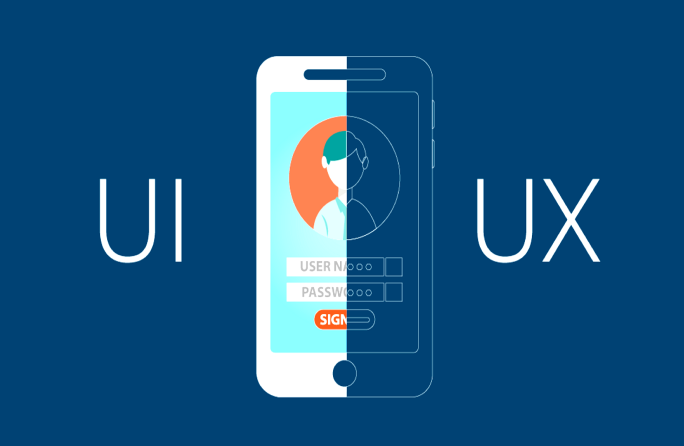

Topics Focused on User Experience
- User experience is concerned with how visitors and users interact with the elements on the site, the flows during their interaction, and the general level of usability.
- It deals with the people who will actually use the design.
- User experience designers work on the general design template and prototypes that can be tested.
- Designers work on the compatibility of elements on the site with each other and the transitions of users between these elements.
- It focuses on the usefulness of the design and the goal of the design.
- It is about solving a certain problem.
- It mostly does these researches and designs by examining the data.